Last updated on August 6th, 2023 at 08:16 am
What is inflation?
The most popular definition of inflation is, “an increase in the average level of prices”. Specifically, inflation is a condition whereby supply persistently fails to keep pace with the expansion of demand.
Simply put, inflation is a state of disequilibrium in which too much money is chasing a few goods. The opposite of inflation is deflation in which there is a fall in the average level of prices.
One consistent factor in the above meaning of inflation is “price”. Price is the monetary value of a product. It could lead to economic instability which is one of the basic problems of an economy. As such, inflation occurs when there is a sustained increase in the monetary value of goods and services in an economy.
Inflation may not be bad in all situations when there is an equal increase in income. For instance, where there is a 5 per cent inflation, and there is also 5 per cent increase in income, 5% inflation may not be an issue because the expenditure takes the same percentage of income
Inflation has become a household name in every part of the world. From Nigeria to Ghana, Canada to the United States, and Germany to Spain, the economic jargon isn’t strange to any student, breadwinners, and buyers of items.
The lives of the rich and average buyers are affected by inflation. That’s why a serious government will never ignore inflation.
Table of Contents
If left uncontrolled, it can dislocate an economy and cause social upheaval. It can cause havoc to an economy and the stability of a country.
In the article, we will shed light on how the rising prices of goods and services can affect the economy of a country.
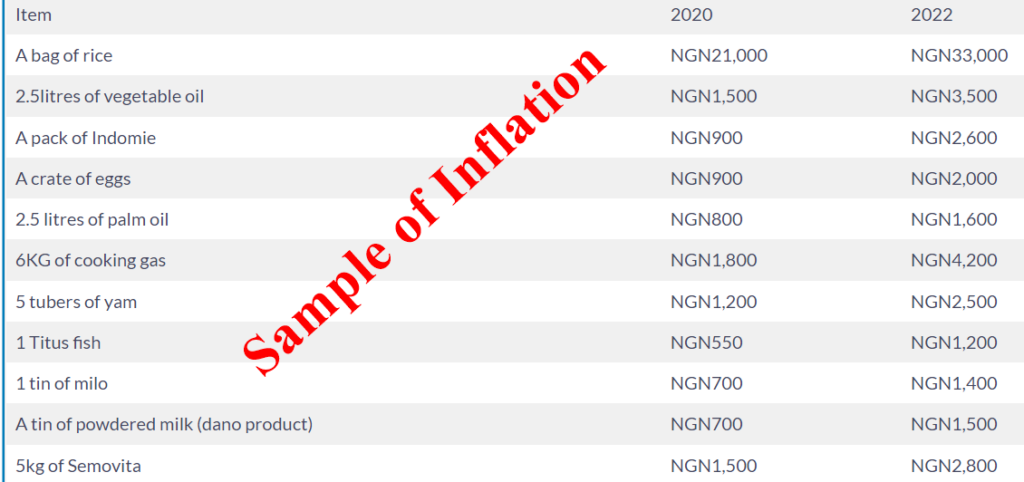
In the table above, where a bag of rice is NGN33,000 ($65.3) in the market while the minimum wage in Nigeria is NGN30,000 ($59.4), there is an issue, workers will fall into poverty.
Example Of Inflation
Below is a list of price changes in household items between 2020 to 2022 for a better understanding of the concept of inflation truly is:
| Item | 2020 | 2022 |
| A bag of rice | NGN21,000 | NGN33,000 |
| 2.5litres of vegetable oil | NGN1,500 | NGN3,500 |
| A pack of Indomie | NGN900 | NGN2,600 |
| A crate of eggs | NGN900 | NGN2,000 |
| 2.5 litres of palm oil | NGN800 | NGN1,600 |
| 6KG of cooking gas | NGN1,800 | NGN4,200 |
| 5 tubers of yam | NGN1,200 | NGN2,500 |
| 1 Titus fish | NGN550 | NGN1,200 |
| 1 tin of milo | NGN700 | NGN1,400 |
| A tin of powdered milk (dano product) | NGN700 | NGN1,500 |
| 5kg of Semovita | NGN1,500 | NGN2,800 |
| A carton of biscuit | NGN700 | NGN1,500 |
Types of Inflation
Generally, inflation can be caused by excessive demand, when this happens, it is called demand inflation or by cost known as costs inflation.
Below are the popular types of inflation that any economy can experience at any given time due to many factors, including poor economic and monetary policies
Demand-Pull Inflation
Demand-pull inflation occurs when demand is high and rising. It occurs when there is more demand for a product than the supply.
This is inflation caused by too much money chasing a few goods. The monetary value inadvertently increases because people have more money or are willing to pay more to own that product.
The buyers bid eagerly for a few goods and services thereby pushing up their prices. In this situation, consumers have more purchasing power to buy goods and services.
Demand increases faster than supply, thereby causing a scarcity which leads to an increase in prices.
Cost-Push Inflation
Cost-push inflation occurs when wages and other costs rise and are passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices for the goods and services on sale.
When there is cost-push inflation, it means the prices of goods and services rise because there is an increase in the cost of production.
Such an increase is passed on to the final consumers. Any economy can experience cost-push inflation because it is quite logical to pass that on to the final consumers.
For instance, Nigeria which has been experiencing a scarcity of forex and exchange rate pressure forced local manufacturers who depend on imported items for production had to increase prices of goods.
Nigerian companies now spend more in accessing forex to import materials for production.
The history of the exchange rate by the CBN has not been palatable and such a trend can not make an investor trust such an economy.
They have to produce, the only option left for them is to increase the price of their finished products. The consumer bear the brunt. That’s a typical example of cost-push inflation.
Built-in Inflation
In Nigeria, whenever there is an increase in wages, the price of goods and services goes up. This means s rise in prices results in higher wages to afford the increased cost of living.
As such, high wages result in an increased cost of production, which in turn has an impact on product pricing. It is an unending circle.
Hyperinflation
Also known as runaway inflation, hyperinflation occurs when the prices of goods skyrocket to an unimaginable level.
Most times, there is hyperinflation when money loses its value due to many factors including when government increases spending.
Runaway inflation is described as an extreme type of inflation by economists around the world. For instance, a pack of noodles (indomie) that was sold for NGN900 in 2020 was sold for NGN2,600 as of March 24, 2022, that’s hyperinflation.
In such a situation, according to Ewa and Agu:
“People are anxious to spend money quickly as possible while they can still get something in exchange for it.”
Hyperinflation Caused By Government
If a government prints money to cover government spending and debt, it pushes up the price of goods astronomically thereby causing runaway inflation.
For instance, the government of Nigeria under the leadership of Muhammadu Buhari in 2021 directed the Central Bank of Nigeria to print more money to be shared as monthly allocation among the three tiers of government (FG, 36 states, and 774 local government areas).
At a time, the government also printed money to pay its civil service. It runs to the CBN to print Naira any time there is a shortage of money
Note:
Demand-push and hyperinflation go hand-in-hand. When there is too much money around, prices skyrocket.
This also brings along with it demand-push because the consumers expect continued inflation, they resort to panic buying, they stockpile goods thereby pushing the price up.
Solution to hyperinflation
One of the solutions to runaway inflation is for the government to tighten the money supply
Open Inflation
When the price level continues to rise and is noticeable by the consumers or buyers, is it called open inflation. Something you bought for NGN40 in January 2022 becomes NGN45. You can see the monthly or annual rate of increase in the price level.
Repressed Inflation
So there is a continued increase in the price of goods and the government realises it. The government comes in with its repressive measures in form of price control which is aimed at preventing the excess demand from increasing the prices, it is called repressed inflation.
Creeping Inflation
Creeping inflation occurs when the price level increases slowly over an extended period of time.
Let’s assume an item that sold for NGN20 in November 2021 now sells for NGN21 (March 2022), it’s creeping. It is called mild inflation.
Mild inflation can boost economic growth because it can drive consumers to demand such goods because they expect that prices will keep going up. It’s now left for the government to set its target inflation rate for proper control.
Stagflation
This happens when an economy is stagnant while there still is price inflation. It sounds contradictory and it happens in rare situations.
The United States experienced this uncommon inflation in the 1970s when it abandoned the gold standard. Once the dollar’s value was no longer tied to gold, it plummeted. At the same time, the price of gold skyrocketed.
To control the stagflation, the head of U.S. Federal Reserve Chairman had to raise the fed funds rate to double-digits.
Galloping Inflation
An economy can lose the credibility and trust of foreign investors when inflation rises to 10 per cent or more. It means money and investment will lose value quickly.
When there is galloping inflation, business and employee income can’t keep up with costs and prices.
The effect is enormous in an economy. For foreign investors who invested $50,000 in January 2021, that value may not be up to $45,000 by January 2022 (in Nigeria).
Investors are mostly forced to withdraw their investment while others look elsewhere to invest.
What are the main causes of inflation?
Many factors are responsible for inflation. They include poor economic policies, disjointed monetary policies, insecurity, and forex scarcity for an importing economy among others.
Poor Monetary Policy
Monetary policy determines the supply of currency in the market. Excess supply of money leads to inflation because it will decrease the value of the currency.
In April 2021, Governor Godwin Obaseki of Edo State, South-South zone of Nigeria spilt the beans when he revealed that the Ministry of Finance in alliance with the Central Bank of Nigeria led by Godwin Emefiele printed NGN60 billion to top-up the federal allocation for March 2021.
Printing money to be shared among tiers of government is a poor monetary policy that leads to inflation.
He was quoted by TheCable as saying:
“So we have run a very strange economy and a strange presidential system where the local, state and federal government, at the end of the month, go and earn salary. We are the only country in the world that does that.”
TheCable
Poor Fiscal Policy
Poor fiscal policy is another cause of inflation. For instance, higher borrowings (debt), result in increased taxes and additional currency printing to repay the debt, this is a situation Nigeria has found itself.
Exchange Rates
Exposure to foreign markets is based on the dollar value. At the time of publication, there the CBN rations USD, Euro, Pounds for buyers thereby pushing them into the black market
At the black market, a USD was NGN580 as of March 25, 2022. Fluctuations in the exchange rate have an impact on the rate of inflation.
Inflation Caused by Insecurity
Inflation caused by insecurity occurs when farmers are unable to access their farmlands because of fear of being kidnapped by terrorists or bandits in some parts of the North has caused an increase in the price of foods in Nigeria.
For instance, onions, pepper, sweet potatoes, corn are majorly cultivated in large quantities by the Northern farmers.
But most of them have been forced to abandon their farmland because of insecurity, hence the increasing rate of food prices in Nigeria.
What are the effects of Inflation?
Those who lived o fixed income will be affected by inflation, the value of money will be reduced and importing economy will also feel the brunt of inflation.
Below are the effects of inflation on an economy and individuals
Effect on Balance of Payment
Inflation can affect a country’s balance of payment, especially for a country that depends largely on foreign trade.
Imports of consumer goods will increase as they become more competitive with home-made goods and as money incomes rise.
Exports will be discouraged because exported goods are relatively more expensive. Also, manufacturers find it easy to sell on the buoyant home market.
These may lead to difficulties in the balance of payments and the government may be forced to check the inflation.
Lead to Poor Saving Culture
Inflation discourages savings because of the fear of losing the value of the money. The real value of the sum saved falls in time.
Hence, people will prefer to spend their money immediately rather than later. Some people used their money to stockpile essential needs with the hope of avoiding further inflation.
It Affects People Living on Fixed Income
Inflation badly affects people who live on a fixed income. Not just that, those who have saved certain amounts for retirement are also badly affected.
“Inflation leads to undesirable redistribution of income. It reduces the living standard of those earning fixed income”.
New System of Economics by Ewa and Agu (page 136)
Pensioners, retired persons wage earners are the losers when there is inflation.
How Does Inflation Affect the Economy?
Inflation is an interesting economic topic that heads of a country’s Central Bank and the Ministers of Finance around the world pay critical attention to.
Because of the increase in the prices of goods and services, the proportion of income that people spend may increase, hence lower savings and low standards of living.
The value of money also drops, especially if its hyperinflation. In a situation where prices continue to rise, it means more money will be required for purchases.
How do we prevent inflation?
- By changing the monetary policy by adjusting the interest rates. Higher interest rates decrease the demand in the economy.
- By controlling the money supply
- A higher Income Tax rate can reduce spending, hence resulting in lesser demand and inflationary pressures.
- Introducing policies to increase the efficiency and competitiveness of the economy helps in reducing the long term costs.
How To Avoid Inflation
It may be difficult for a fixed salary earner or an average person whose source of income isn’t sufficient to cater for their needs.
But for the rich and big-time shareholders, their best option to avoid inflation is to convert their monies to some other stable currency or commodity (Dollar or Gold).
For instance, we saw Access Bank, one of the biggest financial institutions in Africa, saying it would focus on growth in countries with very strong currencies.
It was also reported by Business Insider Africa that devaluation of the naira was one of the reasons the bank wanted to re-strategising
So, companies that are leaving Nigeria are not doing so because of insecurity, they are also relocating or focusing on economies with moderate inflation.
No wonder country like Iran is battling with the rising cost of goods because its Iranian currency is one of the weakest currencies in Asia.
Who benefits from inflation?
Inflation isn’t entirely bad for the economy or an individual. For instance, moderate inflation can boost an economy if it is professionally handled.
In fact, moderate inflation is better than deflation or falling prices. This is because rising prices encourage businessmen to invest their capital in productive ventures.
New industries are established and existing ones are expanded when there is moderate inflation.
This in turn creates jobs, more people are employed, thereby reducing the number of unemployed people.
So…
Who are the beneficiaries of inflation?
From a lending point of view, borrowers gain because they are able to liquidate debt. They are paying less in terms of the value of money.
If inflation is moderate, investors make more gains. While the consumers may spend more on goods, it a boom for an investor.
For instance, assets investors if held on for a long time will certainly benefit from it.
Recap:
- There is inflation when supply can not keep pace with the expansion of demand.
- The most devastating type of inflation is hyperinflation or runaway inflation
- When inflation is moderate, it can be used to spur production in boost an economy
- Inflation does not affect everyone. Borrowers and investors gain when there is moderate inflation.
The most popular types of inflation are:
- Demand-Pull
- Cost-Push
- Creeping
- Hyperinflation
- Built-in
- Repressed Inflation
- Stagflation
- Galloping Inflation
- Open Inflation
Sources
- Ewa Udu and G.A. Agu. “New System Economics”.
- Louis Johnston (November 19, 2021). “Why today’s inflation is nothing like the inflation of the 1970s”. Minnpost.com. Retrieved February 28, 2022
- Emmanuel Benson (March 24, 2022). “Having established presence in 16 countries, Nigeria’s Access Bank will now focus on growth in countries with very strong currencies”. Businessinsider.com. Retrieved March 26, 2022
- National Bureau of Statistics. “Selected Food Prices Watch (February 2022)”. Nigerianstat.gov.ng. Retrieved March 27, 2022