Last updated on November 28th, 2023 at 03:02 pm
If you are planning to or you already have an existing business in Nigeria, you may need to download a copy of CAMA 2020 (the amended CAMA 1990 (CAP C20, LFN 2004).
Table of Contents
What is CAMA?
CAMA is Company and Allied Matters Act. It is a law that outlines the guidelines for the formation of small businesses, medium enterprises, limited liability companies, unlimited firms, corporations, formation of organisations, and non-governmental organisations in Nigeria.

Amendment of Company and Allied Matters Act
Before now, the Companies and Allied Matters Act, 1990 (CAP C20, LFN 2004) was in use. There were attempts to amend its provisions.
One such was the passage of the amendment in 2018 by Nigeria’s legislative arm, but President Muhammadu Buhari refused to assent and sent it back to the lawmakers to adjust some sections of the bill.
To the joy of the business community in Nigeria, Buhari signed into law CAMA 2020 on August 7, 2020.
The passage and the signing was described by analysts and business stakeholders as Nigeria’s most significant business legislation in 30 years.
Why Signing of CAMA 2020 Is Significant
Company and Allied Matters Act, 2020, is significant because it promotes the ease of doing business as it legalises digital registration of business
1) It promotes a more friendly businesses environment
2) It introduces measures to ensure efficiency in the registration and regulation of businesses
3) It reduces the compliance burden of small and medium enterprises (SMEs)
4) It enhances transparency
During the days of CAMA 1990, one had to queue and spend hours filling forms at the branch offices of the Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC).
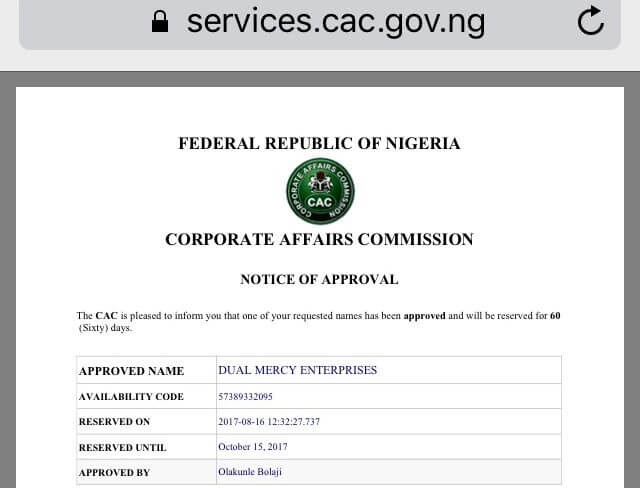
5) With the new CAMA 2020, business/company registration has become easy and faster.
Summary of CAMA 2020
Act has 870 sections which is divided into 7 Parts: A, B, C, D, E, F, and G.
Part A:
Part A of CAMA 2020 has 17 Sections and explicitly covers the formation and responsibilities of the Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC).
CAC is an agency of the government under Nigeria’s Federal Ministry of Industry, Trade, and Investment.
This part contains sections like:
- Annual report.
- Appointment of Registrar-General
- Expenditure of the Commission
- Annual accounts, audit and estimates
Part B:
Part B constitutes appropriately 84% of the Act with 728 sections out of 870 in all. I’m not surprised by this number considering the fact that PART B covers everything about the Incorporation of Companies And Incidental Matters which is further divided into several chapters.
Under this part, you will find interesting topics such as:
- The right to form a business
- Types of companies in Nigeria
- Procedure for changing the name of a company
- Reservation of name etc
Part C:
Part C is entitled “Limited Liability Partnership” and has 49 Sections.
It is also divided into chapters, but the most important thing is that it answers all questions that are related to the formation of limited liability partnership, eligibility to be partners, expiration of partnership among other issues.
If you are planning a partnership business, Part C of CAMA 2020 is your guide, read and adjust to avoid running foul of any part of the law.
Part D:
Part D has 16 Sections and elaborately explains what you need to know about Limited Partnership: what is it, how it is formed, its registration procedure, its constitutions etc.
Part E:
With 12 sections, Part E is the right place you need to digest if you want to understand the intricacies of Business Names.
This part talks extensively about registration of business names, certificate of registration, procedure if you are planning a name change and annual returns of a business among other interesting chapters.
An important aspect of part E is section 815 which covers the procedure for the registration of business names.
Part F:
Part F of CAMA 2020 has 28 sections that cover everything about the management and registration of non-governmental organisation, clubs, associations, community names and associations, and registration of worship centres (churches and mosques).
All these bodies come under Incorporated Trustees and clearly state the exercise of powers of trustees, appointment and suspension of trustees, and their statement of affairs.
Part G:
This part covers the general miscellaneous matters that are not covered by parts A to F. This part contains 20 sections.
How CAMA 2020 Promotes Businesses in Nigeria?
According to statistics by the CAC, the number of registration of business that is being witnessed has grown exponentially since the Company and Allied Matters Act 2020, came into implementation.
For instance, the total of entities registered entities in Nigeria in 2018 was 252,035, but by the end of 2020 (the time CAMA 2020 became law), a total of 353,342 registered entities were recorded.
And a year after – 2021 – the CAC report shows that 652,353 entities were registered comprising business names, companies, and incorporated trustees.
So, how can a business founder take advantage of the provision of the law establishing business in Africa’s largest economy?
CAMA 2020 is promoting businesses in Nigeria in the following ways:
1) CAMA 2020 has eliminated the hurdle business owners pass through in the past, they are now encouraged to either register their business names or commission CAC-certified agent to handle the process for them.
2) It makes it possible to establish a private firm with only one member or shareholder (this can be found in Section 18, sub-section 2).
3) There is a provision for minimum share capital, the promoter of a business doesn’t need to pay for shares that are not needed at a specific time (details of this can be found in Section 27)
4) CAMA 2020 simplifies how business is being done in response to the digitalised business world.
For instance, there is no provision for electronic filing of returns, e-meeting for private companies and electronic share transfer (details of this can be found in section 861 of the new CAMA)
5) Added to the previous points is that the Act promoted virtual Annual General Meetings, provided that such meetings are conducted in accordance with the Articles of Association of the company.
This is in response to the outbreak of COVID-19 which changed the business world. This means location shouldn’t be an hindrance to business meetings.
6) A company that has a single shareholder is no longer mandated to appoint auditors at the annual general meeting to audit the financial records of the company (this can be found in section 402)
7) According to Section 330, subsection 1, the appointment of a Company Secretary is now optional for private companies. This means that appointment of a company secretary is only mandatory for public companies.
8) Creation of new concepts of Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) and Limited Partnerships (LPs) gives prospective business owners the flexibility they need to set up a business.
Do you want a copy of CAMA 2020?
In case you haven’t got a copy, you can download PDF copy of the Company and Allied Matters Act 2020 on CAC Portal or use infomediang download link to keep a copy.