Oyo State is located in southwestern Nigeria, and the city of Ibadan serves as its capital. Oyo State is bounded by Kwara State to the north, Osun State to the east, Ogun State to the southwest, and the Republic of Benin to the south.
The 2016 population estimates by Nigeria’s National Population Commission (NPC) put Oyo State as the 6th most populous state in Nigeria with 7,840,864 people and the 14th largest in Nigeria by area with 28,454 square kilometer.
With the population land area, how viable is Oyo State’s economy? How much does the Pacesetter State generate from Internally Generated Revenue? What is its population distribution?
This article focuses on the major indexes of the economic profile of Oyo State and what the government is doing to improve the revenue of the state.
Oyo State Demography
From 5,580,894 people in the last population census in 2006, the population of Oyo state has grown by adding almost three million people in the 2016 estimates.
The population of men has always been more than the number of women in the Pacesetter State since 2006 till date.
Below is the population distribution of Oyo State: estimates of men and women from 2007 to 2016:
| Year | Male | Female | Total |
| 2007 | 2,944,693 | 2,829,214 | 5,773,907 |
| 2008 | 3,046,534 | 2,927,062 | 5,973,595 |
| 2009 | 3,151,897 | 3,028,293 | 6,180,190 |
| 2010 | 3,260,904 | 3,133,025 | 6,393,929 |
| 2011 | 3,373,681 | 3,241,380 | 6,615,061 |
| 2012 | 3,490,358 | 3,353,482 | 6,843,840 |
| 2013 | 3,611,071 | 3,469,460 | 7,080,532 |
| 2014 | 3,735,959 | 3,589,450 | 7,325,409 |
| 2015 | 3,865,165 | 3,713,590 | 7,578,755 |
| 2016 | 3,998,840 | 3,842,023 | 7,840,864 |
Major business sectors for the Economy of Oyo State
In present-day Oyo, agriculture and handiwork form the economic backbone of the state’s economy. In Oyo today we have several companies and industries such as the British American Tobacco Company (BAT) located in Ibadan uses tobacco, teak, and cotton in their production.
The town has long been renowned as a hub for the cotton industries of spinning, weaving, and dying (with locally grown indigo).
In addition to gourd carving, the region is well-known for its leatherwork (particularly pillows made from goatskin and sheepskin), woodcarving, and matmaking.
Yams, maize (corn), sorghum, cassava (manioc), poultry, okra, and beans are the most often traded agricultural products.
Oyo State IGR and Income Analysis
Ranked No. 17 in terms of GDP, Oyo State has several ways they generate income, one of such is Internally Generally Revenue (IGR) from state taxes and ticketing.
For the most part, state administrations in Nigeria get two distinct streams of income which includes IGR and funds allocated from the Federation Account (also known as Federal Statutory Allocation).
We are, however, more concerned with State-level revenue (IGR). Taxes, fees, licenses, profits, sales, rent on government property, interest, dividends, and stock dividends are some of the internal revenue sources accessible to state governments.
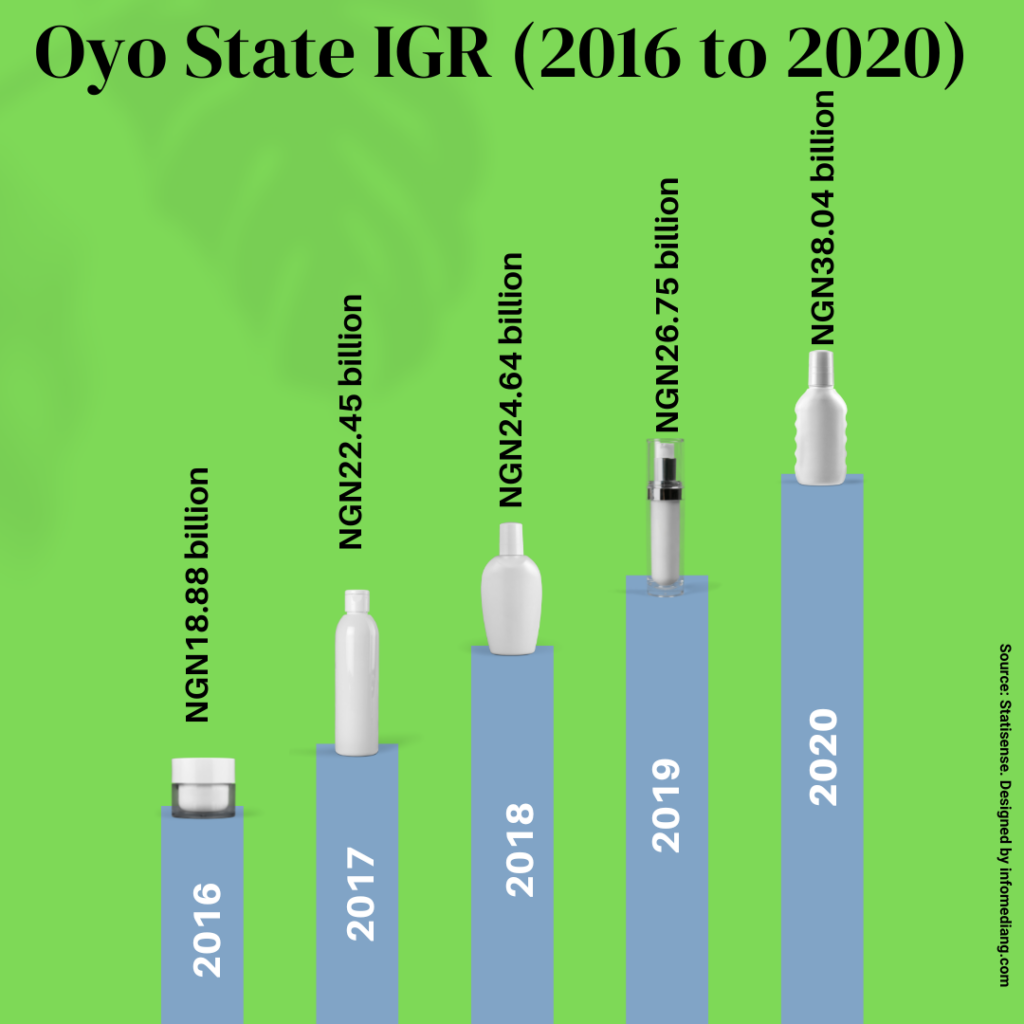
The table below shows how Oyo State government has been able to grow its IGR from NGN8,915,603,182.50 in 2011 to NGN38.04 billion in 2022.
| Year | IGR |
| 2011 | NGN8,915,603,182.50 |
| 2012 | NGN14,598,808,723.10 |
| 2013 | NGN15,251,369,563.24 |
| 2014 | NGN16,307,233,700.20 |
| 2015 | NGN15,663,514,824.73 |
| 2016 | NGN18.88 billion |
| 2017 | NGN22.45 billion |
| 2018 | NGN24.64 billion |
| 2019 | NGN26.75 billion |
| 2020 | NGN38.04 billion |
The government of Oyo State indicated that it is not surprising that it was ranked seventh in the States’ Internally Generated Revenue Index for Q1 and Q2 of 2021 by the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS).
In a report on the states of Nigeria’s IGR for the first half of 2021, NBC revealed that Lagos State (biggest economy in Nigeria by GSP) had the highest total at NGN267.23 billion, followed by the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) at NGN69,072,879,664.43 and Rivers State at NGN57,324,672,372.42.
With total revenue of NGN25, 191,713,455.75, Oyo State ranked seventh in the nation. In terms of money coming in, the state made N78.2 billion.
The report also revealed that Pay As You Earn (PAYE) was the primary source of income for many states in the South-West, with Lagos bringing in NGN152.7 billion and Oyo State coming in at number two with N18.6bn. This disparity in revenue between the two states reflects the relative strength of the labor force in each region.
The amount realized as IGR was NGN16.2 billion, which is 31.49% of the total revenue of the state, while the amount allocated by the Statutory Allocation of the Federation Account Allocation Committee was NGN17.13 billion, which makes 62.29% of the state’s total revenue. The state Government has anticipated NGN79,796,513,040.00 in yearly IGR for 2022.
Economic Polices of The State Towards Growth
Establishing Point-of-Sale (POS) Machines to Reduce Revenue Leakage, Eliminate Cash Handling, and Simplify Revenue Collection. With POS in place, IGR increased to N228 million in August–October 2016 from N155 million in May–July 2016.
Increasing the number of taxpayers who pay taxes using Taxpayer Identification Numbers (TINs) and expanding existing tax bases.
Establishing a Unit for the Informal Economic Sector: Communicating with Street Vendors and Artists via Trade Organizations, Taxi Drivers via the National Union of Road Transportation Workers, etc.
Increased dedication to enforcement and enhanced efforts to improve compliance. Requiring MDAs to take action to recoup revenue.
The improvement in revenue generated by Ministries from about N143 million to around N48 million between September 2015 and April 2016 is a direct result of the collaboration with all MDAs through frequent discussions on the way forward.
The staff of the Board of Internal Revenue conducts regular Tax drives to locate new taxpayers, educate them on the tax payment process, and verify that their taxes have been paid.
The government’s plans to boost the economy through agribusiness and infrastructure development are starting to bear fruit, as seen by the initiatives currently underway.
There is little doubt that in the following months and years, the state government will get more money as a result of the business-friendly policies and the provision of many incentives to investors.
The state government plans to grow the state’s economy through a three-pronged strategy: bolstering the state’s agribusiness sector to lure major investments, strengthening the state’s economic infrastructure, and enacting well-considered policies and incentives that will make doing business easy for investors.
Also, increases in the IGR index can be attributed in large part to the state’s improved ability to timely pay employee salaries and pensions, as well as to the massive completed and ongoing infrastructure development projects and investments in improving security that has improved the business environment.
Remember that Oyo State’s IGR increased by 42.23 per cent between 2019 and 2020, from NGN26.75 billion to NGN38.04 billion?
That’s a lot more growth than the 8.57 per cent increase from 2018 to 2019 when IGR increased from NGN24.64 billion to NGN26.75 billion.
Major Companies in Oyo State
There are many businesses (large and small scale) because of many investment opportunities in the Pacesetter State, below are some of them:
- Ajanla Farms
- Rontol Farms
- Bode foam
- Nipo Factory
- Afriplast industries Ltd
- Nigerian Eagle flour mill
- cool FTN cocoa process plc
- Mountain market Ibadan
- Premier feeds mill company ltd
- Eagle flour
- Stop hunger cassava processing center
- Okiki Ade palm kernel industry
- Sumal food limited (take note Sumal and Yale are different companies owned by the same family)
- Yale Food nig Ltd
- Oriental foods industry Ltd
- Sweetco Foods Ltd
- Quality foods manufacturing Enterprise Ltd
- Energy food company Ltd
- Blue Sapphire Foods
- Belloue Foods
- Blessed food and Drinks company
- Fuman Nigerian limited
- Expanded Global industries
- Heritage coatings and allied chemical products
- Siperco Nigerian Ltd Ibadan
- Glassy liquid Starch Ibadan
- Isogloss industries limited
- AA Olatunji & Sons Nigeria limited (Recycling center)
- Itele Footwear
- Swordcraft steel construction
- Vina international limited
- Fabex paint
- Associated match industries Nigerian limited
- Nestle flower gate factory
- Meyer paints factory
- British American Tobacco factory.
- Nampack carton factory
- Nigerian breweries factory
- International breweries factory
- Nigerian bottling company factory
- 7 up bottling company
- Fan milk factory
- P&G factory etc.
Conclusion:
Oyo State’s economy dwells more on revenues in taxes from the small-medium and large-scale farms spread across the state.
More can still be done to expand the revenue of the state so that it doesn’t depend on the monthly allocation from the federal government.
Oyo State is home to the leading agricultural input fabricators and agro-processors in Nigeria and it is hoped that the state uses this comparative cost advantage to boost its agriculture products.
References
- OYSIPA. “Agriculture and Agribusiness”. oysipa.oy.gov.ng
- Inside Oyo. “Oyo State Ranked 7th On NBS’s States’ Half-year IGR Index”. insideoyo.com
- National Population Commission Estimates: 2007 to 2016
- StatiSense (April 16, 2021). “Oyo State’s IGR – Last 5 years”. twitter.com/StatiSense

